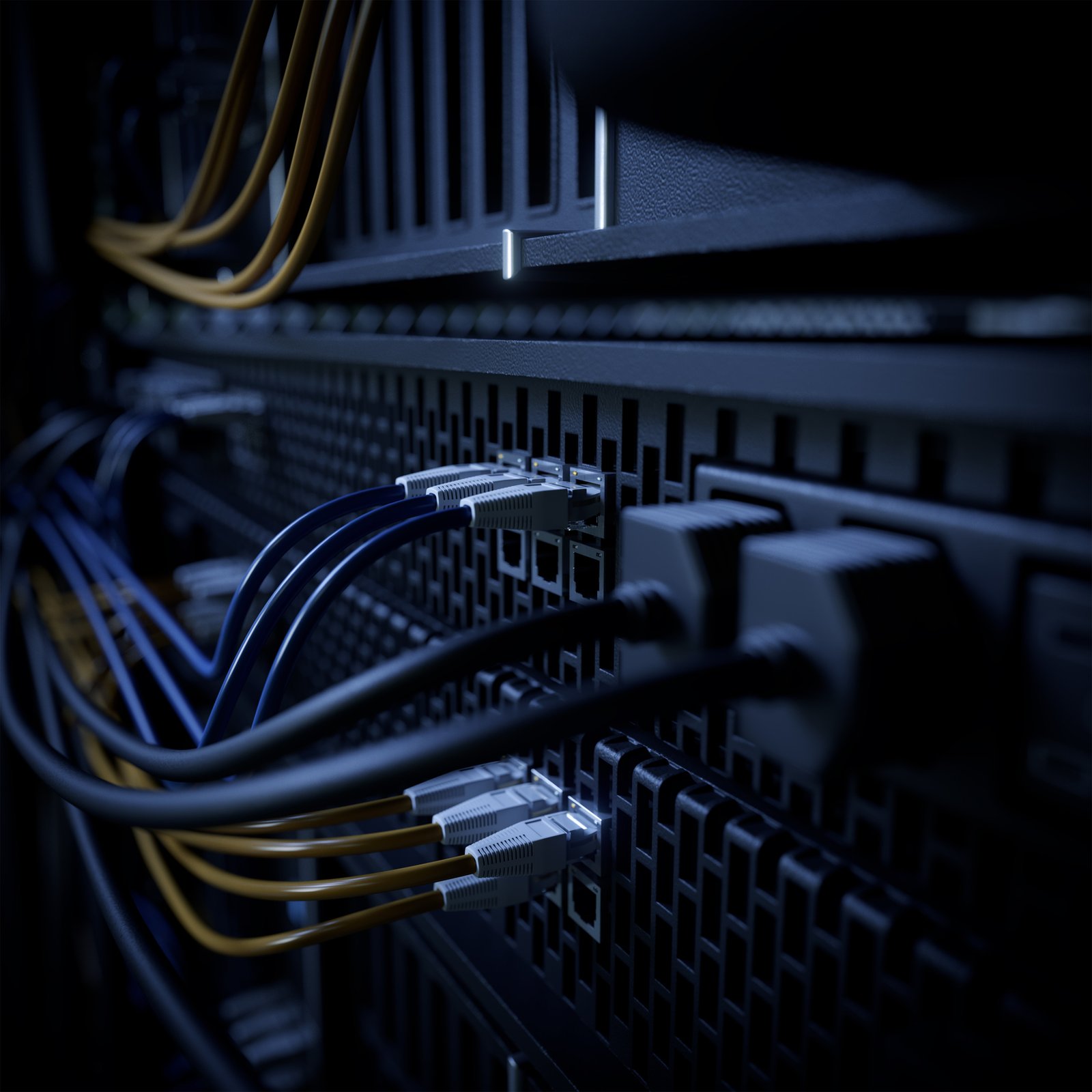
Today’s digital-first world is made possible by the robust infrastructure of data centers, where the demand for data storage and processing grows exponentially almost daily.
These massive facilities house the servers that power our online activities, from streaming videos to storing critical business information.
To meet data demands, data centers are evolving to become more compact and efficient, leading to the rise of high-density data center environments.
“The high-density data center is the future of data management,” says Colocation America.
The Need for High-Density Data Centers
High-density data centers pack more computing power into a smaller footprint. This is achieved by using denser server racks and optimizing airflow for efficient cooling.
These environments are crucial for:
- Cloud Computing: The insatiable appetite of cloud service providers for vast data storage and processing capabilities finds fulfillment in high-density data centers. As more businesses migrate their operations to the cloud, the demand for high-density infrastructure continues to soar.
- Big Data Analytics: Businesses grappling with overwhelming data volumes rely on high-density data centers to navigate intricate data analysis tasks efficiently. The ability to process and analyze massive datasets in real-time is crucial for gaining valuable insights and making data-driven decisions.
- The Internet of Things (IoT): The growing legion of interconnected devices leads to ever-widening data streams, necessitating high-density data centers to manage and process this deluge. From smart homes to industrial IoT applications, the proliferation of connected devices requires robust and scalable data center infrastructure.
- Edge Computing: As the need for low-latency data processing grows, edge computing brings data centers closer to the data sources. High-density edge data centers enable faster data processing and reduced network congestion, enhancing the performance of latency-sensitive applications.
However, packing more computing power into a smaller space creates unique challenges.
Challenges of High-Density Data Centers
While high-density data centers are the answer to modern-day computing issues, they present some challenges themselves including:
- Increased Bandwidth Prerequisites: High-density environments mandate high-speed connections between servers and storage devices to contend with an increased volume of data traffic. As data volumes continue to grow exponentially, the need for higher bandwidth capacities becomes increasingly critical.
- Space Constraints: Data centers must maximize space utilization while ensuring optimal airflow for cooling. Conventional copper cables occupy significant space, precipitating a bottleneck. The limited real estate within data centers necessitates the adoption of space-efficient cabling solutions.
- Power and Cooling Limitations: High-density settings translate to substantial heat. Conventional copper cables exacerbate this heat generation, further burdening cooling systems and escalating power consumption. Efficient power distribution and advanced cooling techniques are essential to maintain optimal operating conditions.
- Cable Management Complexity: With the increased density of server racks and the abundance of cables, effective cable management becomes a daunting task. Tangled and disorganized cables can impede airflow, hinder maintenance efforts, and increase the risk of downtime.
Fiber Optic Cables: The Solution for High-Density Data Centers
Fiber optic cables are the answer to the challenges faced by high-density data centers. Here's how:
- High Bandwidth Capacity
- Single-mode and Multi-mode Fiber: Fiber optic cables transmit data through light pulses, facilitating substantially higher bandwidth compared to copper cables. Single-mode fiber, with its smaller core size, enables longer transmission distances and higher bandwidth, while multimode fiber is ideal for shorter distances within data centers.
- Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM): WDM technology empowers the transmission of multiple data streams on a single fiber optic cable, augmenting its capacity manifold. By utilizing different wavelengths of light, WDM allows for the simultaneous transmission of multiple data channels, significantly increasing the overall bandwidth.
- Space Efficiency
- Reduced Cable Diameter: Fiber optic cables boast a slender profile compared to copper cables, permitting the routing of more cables through the same space. This space efficiency is particularly crucial in high-density environments where every inch counts.
- Augmented Port Density: Network equipment tailored for fiber optic connections can accommodate more ports within the same footprint, optimizing space utilization. High-density fiber patch panels and switches enable the consolidation of numerous connections in a compact form factor.
- Power and Cooling Efficiency
- Diminished Power Consumption: Unlike copper cables that conduct electricity and generate heat, fiber optic cables transmit data via light, consuming substantially less power. This reduced power consumption translates to lower energy costs and a smaller carbon footprint for data centers.
- Mitigated Heat Generation: The diminished power consumption of fiber optics translates to reduced heat generation, alleviating the strain on cooling systems and curbing overall power consumption. By minimizing heat generation at the source, fiber optic cables contribute to a more efficient and sustainable cooling infrastructure.
- Enhanced Signal Integrity and Security
- Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference: Fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), ensuring the integrity and reliability of data transmission. In high-density environments where numerous cables are tightly packed, this immunity is particularly valuable.
- Improved Data Security: Fiber optic cables offer inherent security advantages over copper cables. They do not radiate electromagnetic signals, making it extremely difficult to intercept or eavesdrop on the transmitted data. Enhancing security is crucial for protecting sensitive information in data centers.
Implementing Fiber Optic Cables in High-Density Data Centers
To harness the benefits of fiber optics in high-density environments, proper implementation is imperative. Experience has taught DCS to look for the following:
- Structured Cabling Systems
- Scalable Modular Design: Structured cabling systems furnish a modular infrastructure conducive to facile expansion and reconfiguration as data center requisites evolve. By adopting a structured approach, data centers can easily accommodate growth and adapt to changing requirements.
- Efficient Cable Management: These systems proffer organized conduits for routing cables, curbing clutter, and enhancing airflow for superior cooling. Proper cable management techniques, such as using cable trays, labeling, and color-coding, streamline maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
- Fiber Optic Connector Types
- LC, SC, and MPO Connectors: Tailored for fiber optic cables, these connectors furnish secure and efficient connections. LC connectors offer a compact form factor, while SC connectors provide a reliable and sturdy connection. MPO connectors enable high-density connectivity, allowing multiple fibers to be connected simultaneously.
- High-density Fiber Patch Panels: These panels facilitate the termination and management of multiple fiber optic cables in a compact and systematic manner. They offer a centralized point for organizing and connecting fiber cables, simplifying cable management, and reducing clutter.
- Best Practices for Installation and Maintenance
- Prudent Handling and Cleaning Protocols: Fiber optic cables, owing to their delicacy, require proper handling to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance. Proper cleaning techniques, such as using lint-free wipes and specialized cleaning fluids, prevent contamination and maintain the integrity of the fiber connections.
- Routine Testing and Monitoring: Regular testing of fiber optic connections is imperative to pinpoint and rectify potential issues before they impinge on network performance. Employing advanced testing equipment and monitoring tools helps detect and diagnose problems promptly, minimizing downtime and ensuring optimal network health.
Future-proofing High-Density Data Centers with Fiber Optics
Innovation is needed in the data center industry to keep up with the ever-increasing data demands. Fiber optic technology has been evolving to meet these ramped-up requirements.
“As new technologies place increased demand on data centers, companies are experimenting with a new generation of superfast fiber-optic networks,” reported Data Center Knowledge in January 2024. “When it comes to new, data-hungry technologies such as AI, the discourse is often focused on new chips and other hardware for training LLMs and reducing ‘next-token latency.’ However, fiber-optic networks remain an integral part of today’s digital infrastructure, not only in terms of the data that flows between IT facilities but also back and forth to end users.
Here’s a peek at how fiber optic technology is playing a role in future-proofing high-density data centers:
- Emerging Technologies: Advancements such as 400G and beyond transmission speeds and silicon photonics integration augur even higher bandwidth capacity and enhanced efficiency in the offing. These cutting-edge technologies promise to revolutionize data center connectivity, enabling unprecedented data transfer rates and reducing power consumption.
- Preempting Future Bandwidth Demands: By embracing fiber optic technology today, data centers can fortify their infrastructure to tackle future bandwidth needs without triggering major upgrades. Investing in a solid fiber optic foundation ensures that data centers are well-equipped to handle the ever-growing data demands.
- Seamless Integration with Emerging Architectures: Fiber optic cables seamlessly integrate with emerging data center architectures, such as leaf-spine networks and software-defined networking (SDN). These architectures leverage the high bandwidth and low latency of fiber optics to enable agile, scalable, and programmable data center networks.
High-density data centers are at the forefront of today’s data storage and processing demands, and fiber optic cables have emerged as a key player in facilitating these environments by offering unparalleled bandwidth capacity, as well as space, power, and cooling efficiency.
By harnessing the power of fiber optic cables, data centers can not only meet the challenges of today but also lay the foundation for a future wherever our digital world may take us.